Chatbot
Accessibility with Chatbots: Definition + Implementation
Starting on June 28, 2025, the Accessibility Strengthening Act will come into effect - is your website up-to-date? What needs to be considered for accessible and inclusive websites and chatbots? You can find out in this article.
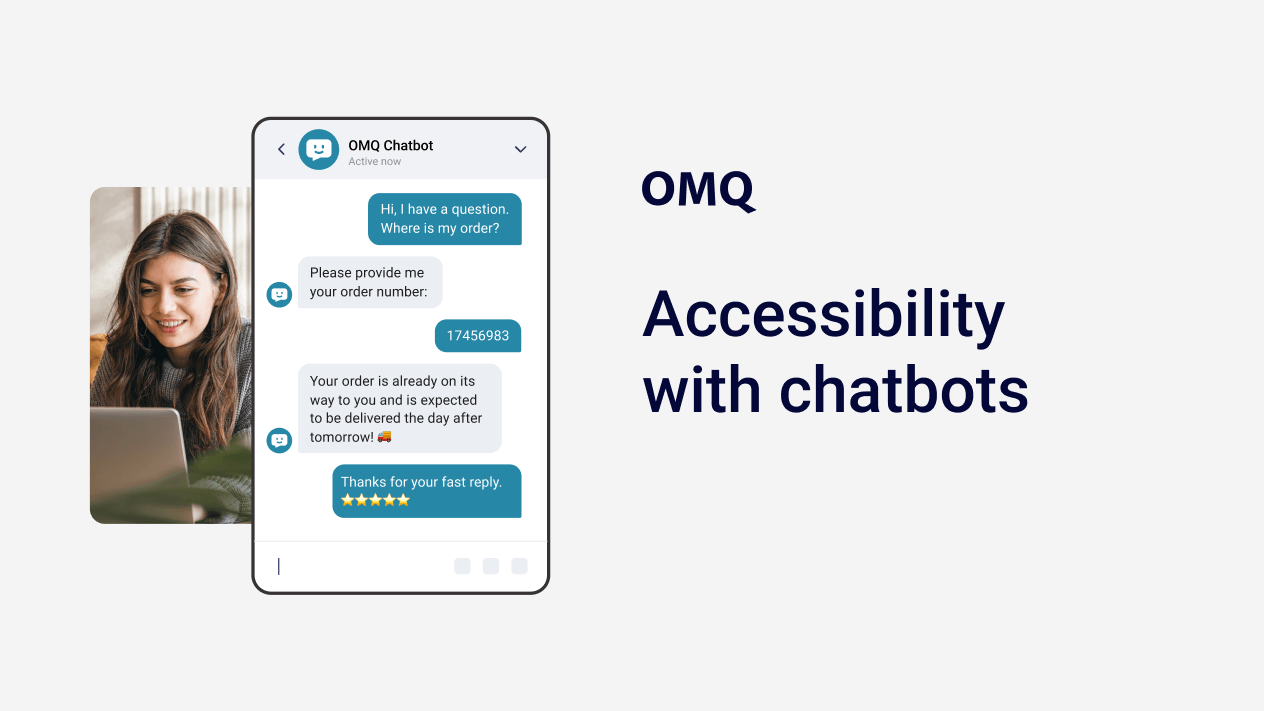
The new year has just begun and many companies have set themselves various goals and resolutions that they want to implement over the next few months - but have they also thought about the Barrierefreiheitsstärkungsgesetz (BFSG)?
The BFSG was passed on June 15, 2022 and defines accessibility requirements for products and services that are placed on the market or provided after June 28, 2025. This includes, among other things, all online trade, hardware, software, but also passenger transport or banking services.Federal Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs
… So how do you make a website accessible? What exactly does the law cover, what guidelines are there? What is an “accessible chatbot”? We will explore these questions in this article.
- What is Accessibility?
- Accessible Digitization
- What is the BFSG?
- What Regulations and Requirements does the Accessibility Strengthening Act include?
- What does an Accessible Website look like?
- Accessibility with Chatbots
- What makes a Chatbot accessible?
- Importance of Accessibility in the Digital Age
- Conclusion
What is Accessibility?
For most people, inclusion means that buildings are more accessible, for example by installing ramps or elevators, or that public transport can be lowered.
According to Aktion Mensch, accessibility means that buildings and public spaces, workplaces and apartments, means of transport and everyday objects, services and leisure activities are designed in such a way that they are accessible to everyone without outside help.
However, this not only includes our everyday environment, but also the digital space.
In Germany there are about 13 million people with disabilities - around 8 million of them are severely disabled.Federal Government Commissioner for Matters relating to Persons with Disabilities
Accessible Digitization
Digital accessibility refers to the design and development of digital content, platforms and technologies in such a way that they are accessible and usable for all people, regardless of their individual abilities or disabilities.
The aim is to remove barriers that could prevent people with disabilities from accessing digital information and services.
Main components of digital accessibility:
- Website design: Websites should be designed to be compatible with assistive technologies such as screen readers. This includes the use of semantic HTML and the provision of alternative text for images.
- Multimedia content: Videos should include subtitles or transcripts to be accessible to people with hearing impairments. Audio files should also be supplemented by text transcripts.
- Navigation: Navigation should be simple and intuitive so that users with cognitive impairments can easily navigate through the content. All functions should also be accessible via the keyboard.
- Text design: Texts should be written in clear and simple language, with the option of adjusting the font size and color for better readability.
- Interactive elements: Forms and other interactive elements should be designed to be accessible to ensure that they can be filled out by all users.

Checklist for an accessible website.
Digital accessibility is not only an ethical obligation, but also often a legal requirement in many countries. It contributes to creating a more inclusive society by ensuring that no one is excluded due to digital barriers.
What is the BFSG?
The Barrierefreiheitsstärkungsgesetz (transl. Accessibility Strengthening Act) is a German law aimed at improving digital accessibility. It comes into force on June 28, 2025 and requires websites, apps and other digital content to be accessible to people with disabilities.
The law was introduced to ensure that all people, regardless of their abilities or impairments, have equal access to digital information and services. This is an important step in promoting inclusion and preventing discrimination in the digital space.
The BFSG implements the EU Directive on Accessibility (European Accessibility Act, EAA for short). The aim of uniform EU requirements is to help small and medium-sized enterprises to exploit the opportunities of the European single market (you can find out more about this on the website of the Federal Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs and the Portal for Accessibility).
What Regulations and Requirements does the Accessibility Strengthening Act include?
The Accessibility Strengthening Act (BFSG) includes a number of regulations and requirements aimed at making digital content and services accessible to people with disabilities. The most important aspects of the BFSG include:
- Accessibility of websites and apps: The law requires that all websites and mobile applications must be designed to be accessible. This means that they should be developed in such a way that they can also be used by people with various disabilities.
- Inclusion of public and private sectors: While the law initially affects public bodies, it is increasingly becoming relevant for private companies that offer digital services.
- Technical standards: The BFSG defines technical standards that must be observed when developing digital content. This includes, for example, the use of semantic HTML5, ARIA attributes and other technologies that ensure compatibility with assistive technologies such as screen readers.
- Obligation to provide alternative communication channels: Companies and organizations must offer alternative communication options to ensure that all users have access to their services.
- Training and awareness-raising: The law also promotes the training of developers and designers in accessible practices and raising public awareness of the importance of digital accessibility.
Through these measures, the BFSG aims to create a more inclusive digital environment and ensure that no one is excluded due to barriers on the Internet.
What does an Accessible Website look like?
An accessible website is accessible and user-friendly for all users. Restrictions on seeing, hearing, moving and processing should therefore be minimized or completely eliminated.
Concrete barriers are, for example:
Aktion Mensch
- People with visual impairments can hardly see texts or form fields if they only stand out slightly from the background.
- Deaf and hard of hearing people cannot use videos if they do not have subtitles.
- Blind people cannot use websites properly if images, forms and buttons are not described in text.
An accessible website should therefore optimize the following elements to make it more accessible:
- Images and graphics: Image descriptions can help people with visual impairments to capture all elements of a website.
- Videos and audio files: Subtitles, audio descriptions and videos in sign language improve the website experience.
- Texts and headings: Texts should be written in simple or easy language so that they can be understood by as many people as possible.
Accessibility with chatbots
Chatbots have the potential to change the way we interact with digital platforms. But to be truly inclusive, they need to be designed to be accessible to everyone. Accessibility with chatbots means that these technologies are developed in such a way that they can also be used by people with disabilities.
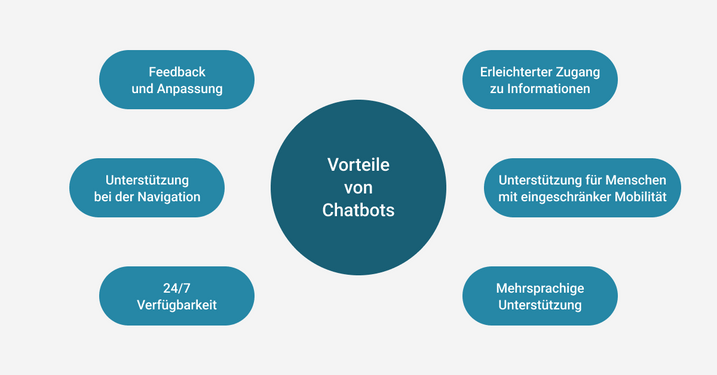
General advantages of a chatbot.
In order to develop an accessible chatbot, a number of tests and methods are required to find out whether there are any difficulties on the part of the users. There are so-called Accessibility Checkers that can be used to scan the chat interface and test it for possible obstacles.
In addition, inclusivity can also be tested yourself by trying out the chatbot with different devices to identify possible weaknesses. Ultimately, user feedback should also be a priority after implementing an accessible chatbot.
What makes a Chatbot accessible?
The chatbot is primarily a visual element on a website. It therefore stands to reason that the chat interface should take into account how color contrast, font and font size, the layout and the spacing harmonize with one another.
The font size should be large enough to be clearly visible on different devices such as computers, laptops, tablets and mobile phones. The font should be kept simple.
Here are some other features and best practices that characterize an accessible chatbot:
- Text alternatives: In addition to text, the chatbot should offer non-textual alternatives, such as voice control or telephone contact, to accommodate users with visual or motor impairments.
- Clear and simple language: The chatbot’s communication should be in clear and simple language to make it easier for all users to understand, especially those with cognitive impairments.
- Keyboard accessibility: All functions of the chatbot should be accessible via the keyboard so that users with motor impairments can operate the chatbot without a mouse.
- Compatibility with screen readers: The chatbot should be programmed to be compatible with screen readers. This includes the use of semantic HTML5 and ARIA attributes.
- Responsive design: The chat window and content should be easy to read and use on different devices and screen sizes.
- Visual customization options: Users should be able to adjust font sizes and contrasts in the chat window to improve readability.
- Error messages and help: The chatbot should display clear error messages and provide assistance if necessary to help users navigate through the conversation.
- Human support: For complex requests, the chatbot should offer the option of forwarding the conversation to human agents.
- Avoid flashing elements: Flashing or fast-moving elements in the chat window should be avoided to minimize distraction and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy.
- Multilingual support: An accessible chatbot should offer multilingual support to cater to users with different language backgrounds.
Importance of Accessibility in the Digital Age
Accessibility is not just a legal requirement, it is also an ethical obligation. It ensures that everyone has equal access to digital information and services. This is particularly important at a time when more and more interactions are taking place online.
Conclusion
Accessibility in the digital space is more than just a legal necessity; it is an essential part of a just and inclusive society. The Accessibility Strengthening Act (BFSG) ensures that digital content and services are accessible to all people, regardless of their abilities. Companies that act now and make their digital offerings accessible are not only investing in meeting legal requirements, but also in a broader customer base and a positive brand perception.
Implementing accessibility requires careful planning and ongoing adjustments. Whether through the design of accessible websites or the development of inclusive chatbots, the focus should always be on the needs of the users. Technology can break down barriers if used wisely. With the right tools and a clear understanding of the principles of accessibility, companies can create a digital environment that is accessible to everyone.
In an increasingly networked world, it is essential that no one is excluded due to digital barriers. Promoting inclusion through accessible technologies is not only an act of fairness, but also a strategic advantage in a diverse society. Companies should seize this opportunity to become pioneers in digital inclusion and thus make a positive contribution to the future of the Internet.