Customer Service
Omnichannel vs. Multichannel
Discover the differences between Omnichannel and Multichannel, and learn how these strategies impact the customer experience. Explore the advantages, challenges, and use cases of both approaches.
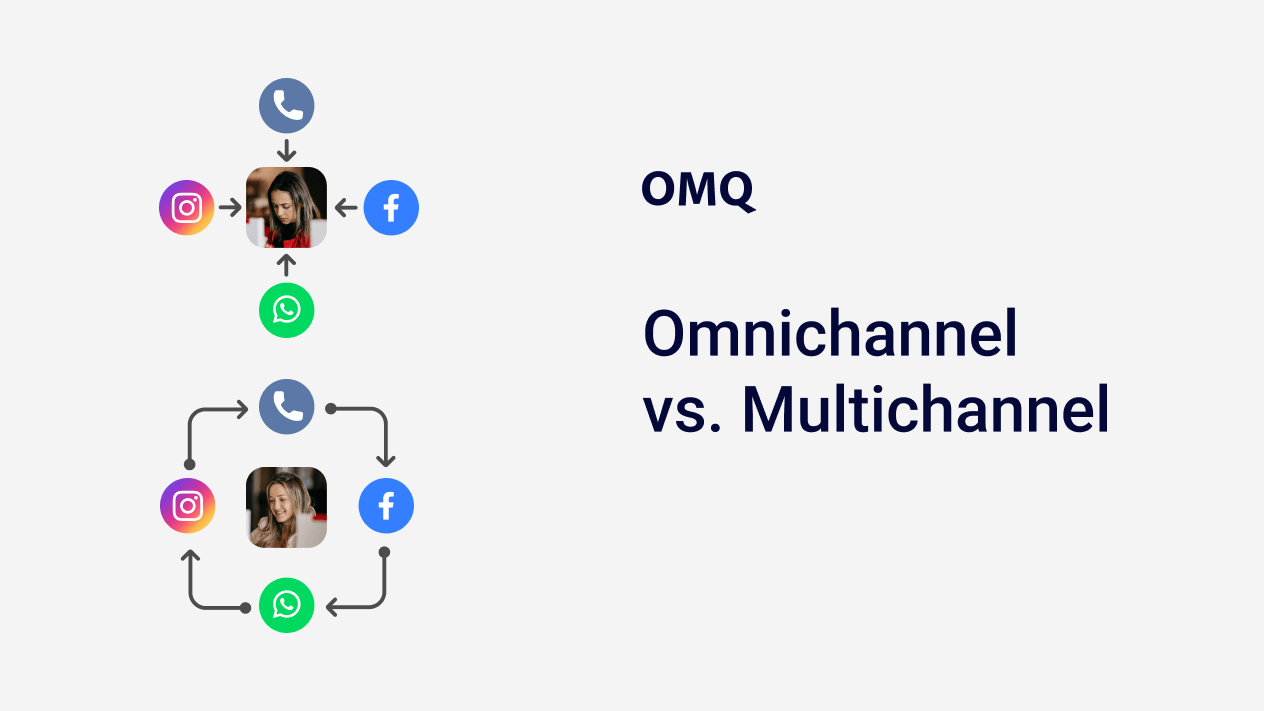
It’s no secret that reaching customers via different channels is an advantage. However, companies face the challenge of finding the right approach to cross-channel customer service.
The terms “omnichannel” and “multichannel” often come up in conversations about marketing strategies, but what do they really mean? And how do they differ from each other?
In this article, we’ll look at the concepts of omnichannel and multichannel, discuss their pros and cons and find out which strategy is best for your business.
Omnichannel vs. Multichannel: Definitions
Omnichannel
The Omnichannel approach aims to create a seamless and integrated customer experience across all communication channels. It is a customer-centric strategy where all channels are interconnected to provide a unified experience.
This means that customers, whether interacting online or offline, enjoy a consistent experience.
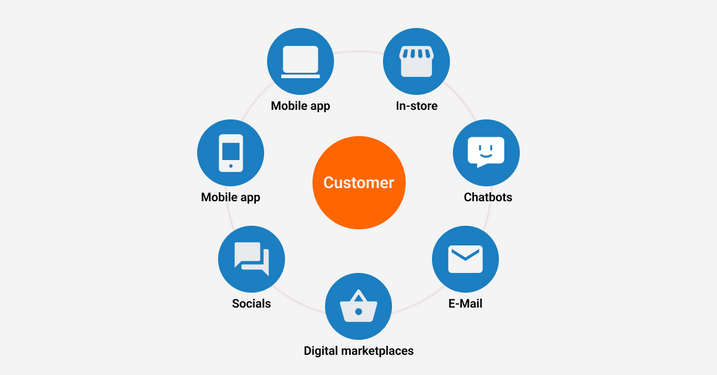
Possible channels for dealing with customers.
Multichannel
In contrast, the Multichannel approach is product-oriented and utilizes various separate channels to interact with customers. These channels often operate in isolation from one another, leading to a fragmented customer experience.
Businesses use multiple platforms to market their products or services without interlinking them.
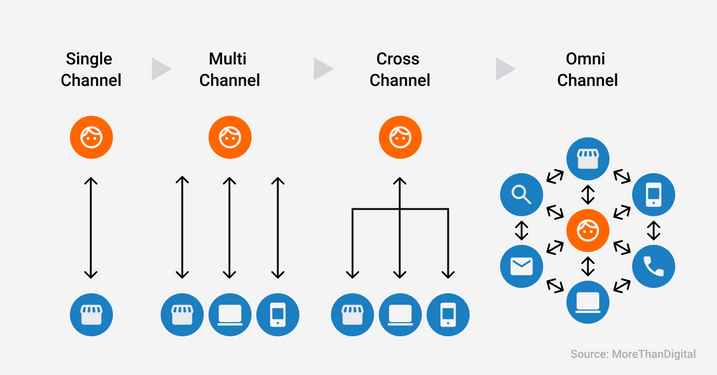
Different approaches for communication channels.
Integration: The Key Difference
The key difference between Omnichannel and Multichannel lies in integration. While Omnichannel systems are fully integrated and offer a holistic view of customer interactions, the Multichannel approach operates in silos without cross-channel integration.
This means that in the Omnichannel model, all data points can be combined to paint a comprehensive picture of customer behavior.
Customer Experience: Consistency vs. Fragmentation
Another significant difference lies in the customer experience. The Omnichannel approach offers a consistent and personalized journey across all channels. In contrast, the experience in the Multichannel approach can be perceived as disjointed due to lack of integration.
Customers might receive different information or offers on one channel compared to another.
Data Usage: Hyper-Personalization vs. Limited Access
Omnichannel leverages complete customer data across all channels for hyper-personalization of the experience. This allows companies to provide tailored offers and content based on each customer’s preferences.
In contrast, the Multichannel approach has limited access to customer history specific to each channel.
Benefits of Omnichannel
Some main benefits of the Omnichannel approach include:
- Unified Customer Experience: Customers enjoy seamless interaction regardless of chosen channel.
- Comprehensive Customer Data: Enables personalized engagements through extensive data insights.
- Adaptability: Flexibility to adapt to new communication channels.
- Productivity Boost: Improved efficiency through integrated systems.
Benefits of Multichannel
The Multichannel approach offers the following advantages:
- Easy Setup: Quick implementation without complex integration requirements.
- Channel Preferences: Allows businesses to engage on their customers’ preferred channels.
- Cost Effectiveness: Affordable for market entry.
- Suitable for Limited Online Presence: Ideal for companies with restricted digital reach.
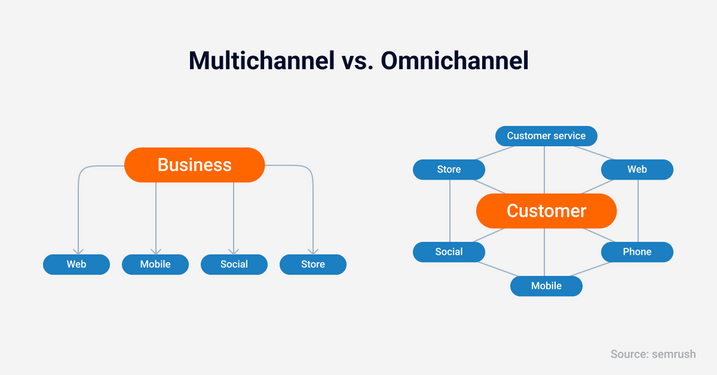
Direct comparison of multichannel and omnichannel.
Implementation Challenges
Implementing Omnichannel and Multichannel solutions in customer service presents businesses with various challenges. One major hurdle is integrating different communication channels into a seamless customer experience.
Companies must ensure that all channels – whether phone, email, social media, or live chat – are interconnected and exchange information in real-time. This often requires significant investments in technology and infrastructure as well as adapting existing systems.
Another issue is training staff to ensure that employees provide consistent and high-quality service across all channels. Additionally, companies must ensure they have necessary data analytics tools to monitor and improve customer interactions.
Despite these challenges, successfully implementing such solutions holds potential for enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty.
When to Choose Each Approach?
Choosing between Omnichannel and Multichannel depends on several factors:
When should you use Omnichannel?
For businesses focusing on enhancing customer experience or serving industries with integrated data management needs (such as healthcare or finance), the Omnichannel approach is ideally suited.
When should you use Multichannel?
Companies with limited resources or specific campaign goals could benefit from adopting a Multichannel model – especially during initial market entry or increasing visibility without extensive integration efforts.
Industry-Specific Examples
To better understand how these approaches work in practice:
Omnichannel Examples:
- Retailers offering both online and brick-and-mortar experiences (e.g., click-and-collect services).
- Companies employing integrated marketing strategies across digital as well as physical channels.
Multichannel Examples:
- Brands selling products on different platforms without integrated customer experiences.
- Firms using separate marketing strategies tailored individually for each channel’s target audience.
Strategic Considerations for Your Decision
When deciding between these two approaches consider:
-
Company Size & Complexity: Larger organizations may benefit from comprehensive approaches; smaller enterprises might find simpler solutions more manageable within multi-channel realms fitting better.
-
Customer Preferences : Omni suits well if your target group regularly interacts cross-platform, while Multi appeals more those whose focus involves clearly defined interactions.
-
Budget & Resources : While Omni demands higher initial investments promising long-term value, Multi appears initially cost-effective yet potentially inefficient if not optimally managed.
Ultimately the choice strongly depends upon specific business objectives sought along with needs held by target audience. Both models possess individual strengths thus possibly even hybrid solutions proving beneficial.


